Case1 – NSCLC Stage IIA (T2N1M0)
Author:
Felix Herth, MD and Ralf Eberhardt, MD, Thoraxklinik, University of Heidelberg, Germany
Source:
DVD-ROM ‘Endoscopic Ultrasound – Diagnostics and Staging of Lung Cancer’, Olympus Europa SE & Co. KG, 2013
Patient History
Farmer, exposition to pathogenic substances.
Urothel Ca, TUR 2004; COPD patient with Emphysema,
St 3; hyperthyreosis. Patient reports symptoms of slight dry cough;
no fewer. Loss of weight 2 kg in 2 months.
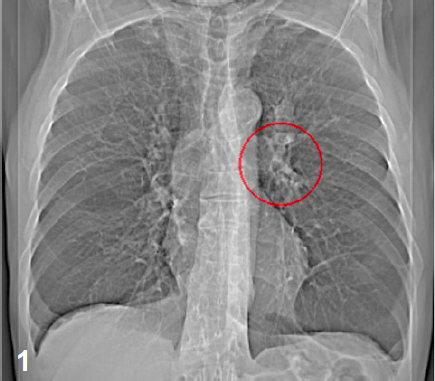
Dyspnoea under stress. Vertigo. Suspicion of CHD. Previous bronchoscopy showed CIS at the dorsal distal right main bronchus. X-ray
Lesion at the left hilus (fig. 1).
CT
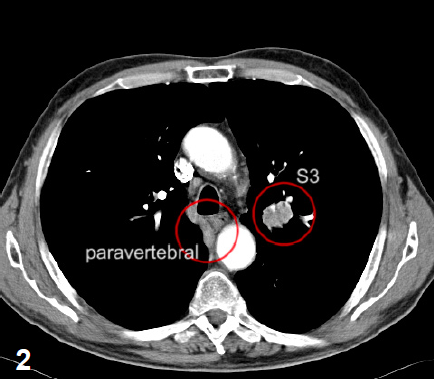
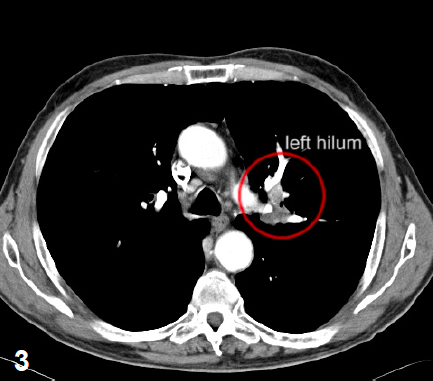
A 31x25mm lesion at segment S3 of the left lung.
A second lesion can be seen at segment 7 paravertebrally.
Several lymph nodes at the left hilum (fig. 2 and 3).
A 31x25mm lesion at segment S3 of the left lung.
A second lesion can be seen at segment 7 paravertebrally.
Several lymph nodes at the left hilum (fig. 2 and 3).
2
3
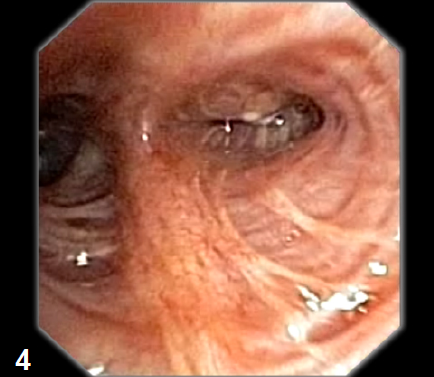
4
Compression of left bronchus segment S3.
Suspicion of LC invasion (fig. 4).
Endobronchial ultrasound
EBUS-TBNA confirms an enlarged lymph node in station 11L (fig. 5).
EBUS-TBNA confirms an enlarged lymph node in station 11L (fig. 5).
5
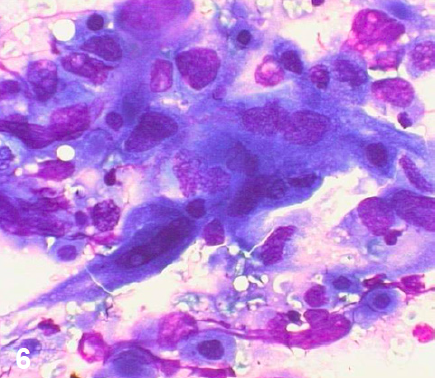
6
Biopsy from the left bronchus segment S3 did not confirm LC invasion. Cytology specimen from LN11L
NSCLC–squamous cell lung cancer (fig. 6). Diagnosis
NSCLC Stage IIA (T2N1M0). Treatment
Due to the increased cardiopulmonary risk the patient was not referred to surgery but to radiation therapy instead. Bronchoscopic control of the CIS (RMB) within the following 6-8 weeks.