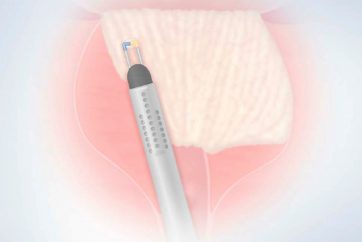
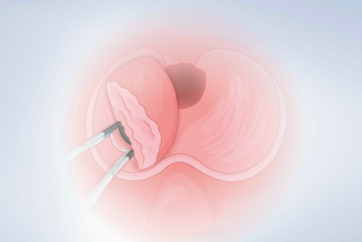
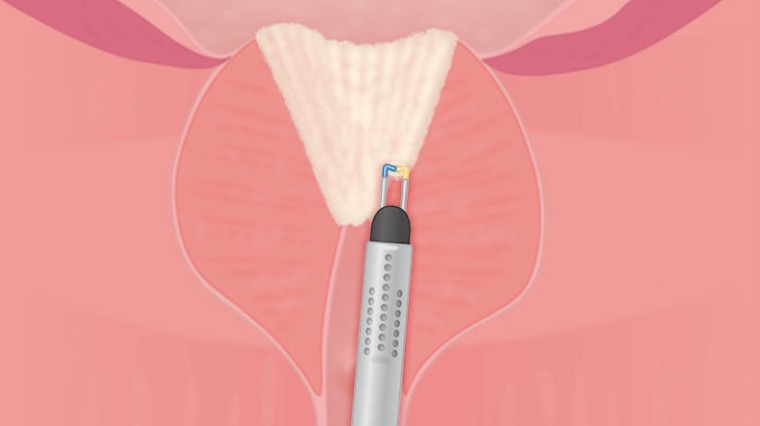
PLASMA Vaporization Procedure Steps – Barnes Method
01|Cystoscopy with Inspection of Urethra
Inspection of the urethra and bladder.
02|Marking of Resection Borders
Marking proximally of the verumontanum in the case of EP procedure.
03|Vaporization of the Medial Lobe, of Basal Portions of Lateral Lobes, and of the Floor of the Prostatic Cavity
Vaporization of medial lobe and proximal part of the side lobes until the 5 o’clock and 7 o’clock position.
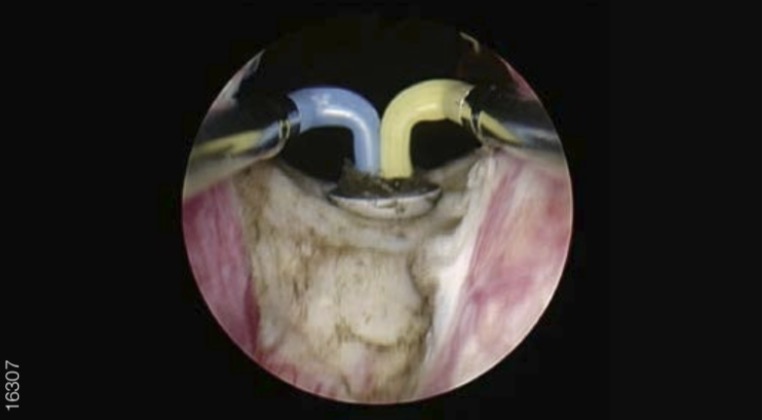
04|Further Ablation of the Endovesical Part of the Medial and of the Left Lateral Lobe
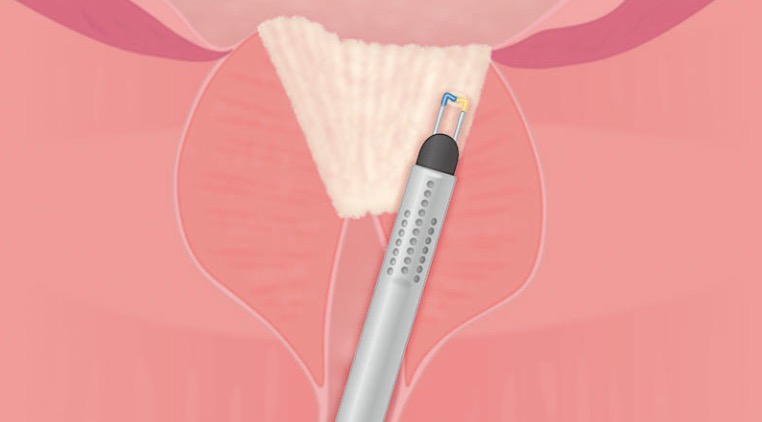
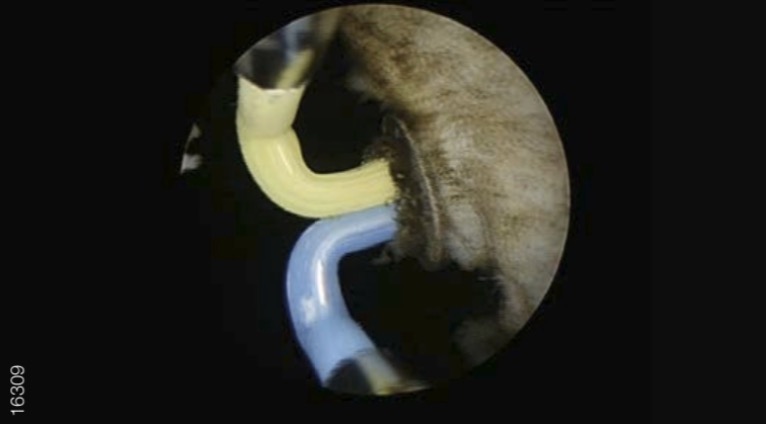
05|Complete Vaporization of the Endourethral Part of the Left Lobe Except for an Apical Remnant


PLASMA VAPORIZATION PROCEDURE STEPS – BARNES METHOD
06|Ablation of the Endovesical Part of the Right Lateral Lobe

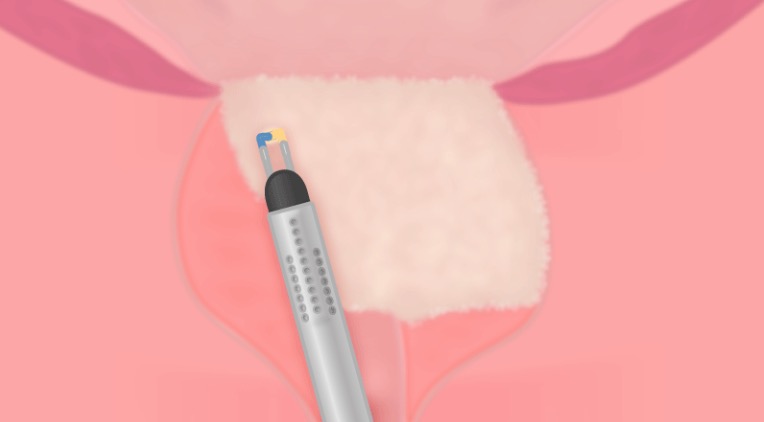
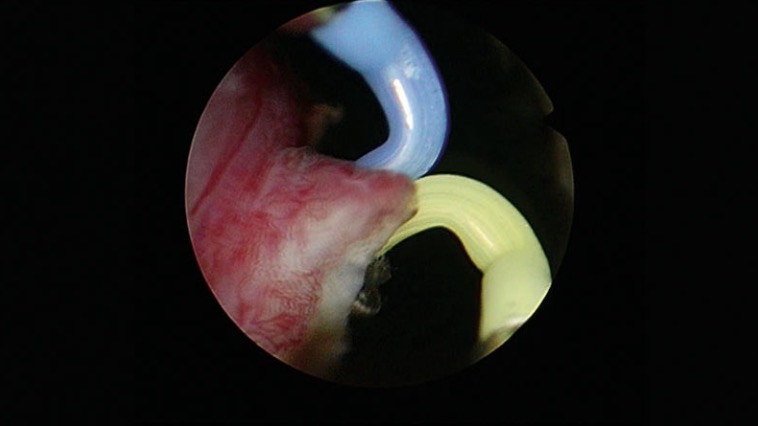
07|Complete Vaporization of the Endourethral Part of the Right Lobe Except for an Apical Remnant
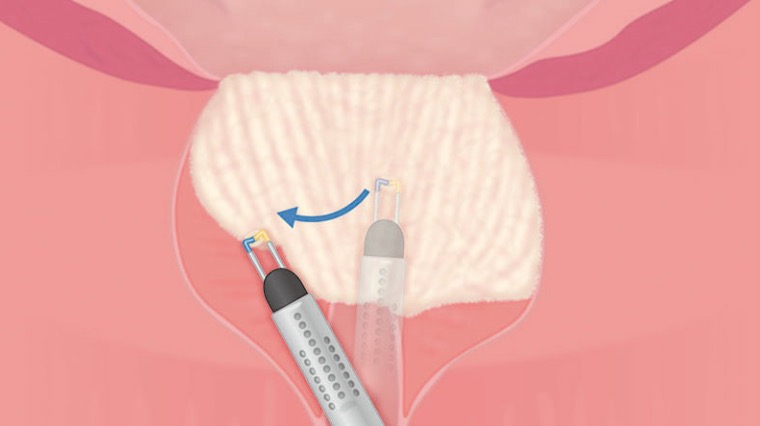
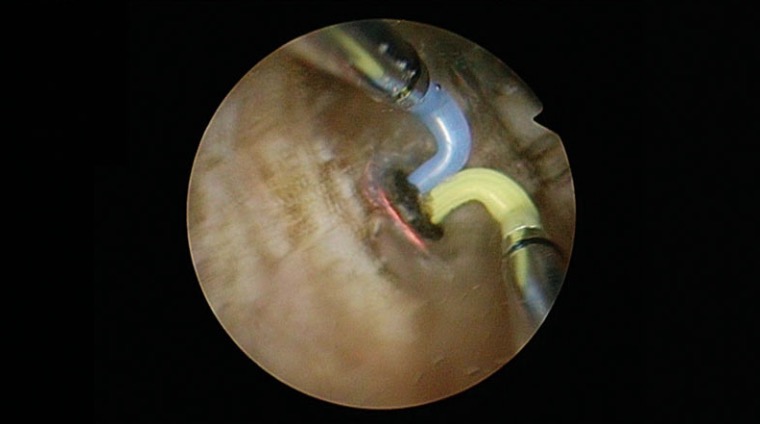
08|Final Vaporization of the Apical Part
To avoid postoperative voiding disturbances, the BPH should be removed completely. At the apex remaining material can be vaporized or resected conventionally.
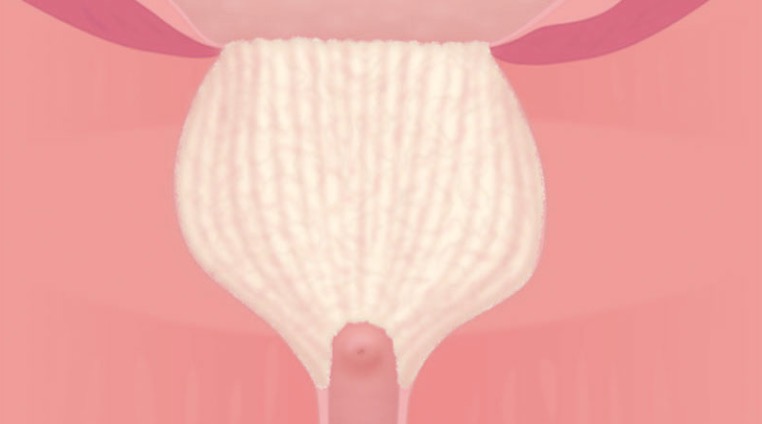
09| Ensure Secure Hemostasis
Be aware of bleeding and do spot coagulation where needed. Place the loop with slight pressure on the bleeding, activate coagulation mode and hold until bleeding has stopped.
The Nesbit Technique
PLASMA Vaporization
10:05
Prof. Dr. Jörg Raßler (Urology Department, St. Elisabeth-Krankenhaus, Leipzig) performing transurethral vaporization of the prostate with Olympus PLASMA technology.
- Content Type