Glottic Squamous Cell Carcinoma

Giorgio Peretti, MD, PhD
Francesco Missale, Andrea Luigi Camillo Carobbio, Frank Rikki Canevari
IRCCS Ospedale Policlinico San Martino, Genoa, Italy
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy
Endoscopic Finding;
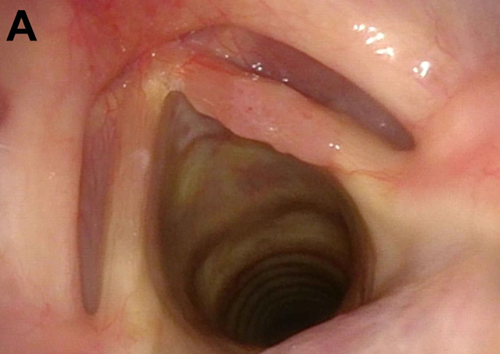
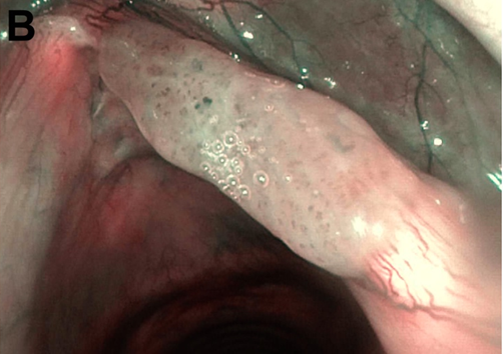
The examination of the glottis in white light (A) revealed an erythroplakia involving the right vocal cord. In NBI observation (B), some atypical perpendicular vascular abnormalities in terms of “dark spots”, clearly observed inside the lesion, raised the suspect of hiding at least a dysplastic transformation. The superficial margins of the lesion were better defined with the use of NBI, not involving the commissures, the ventricle and the subglottis. Vocal cords were mobile, and at the laryngostroboscopy a reduced amplitude of the mucosal wave on the right side was present.
The clinical staging is: cT1a glottic lesion of the right vocal cord.
Pathological Finding;
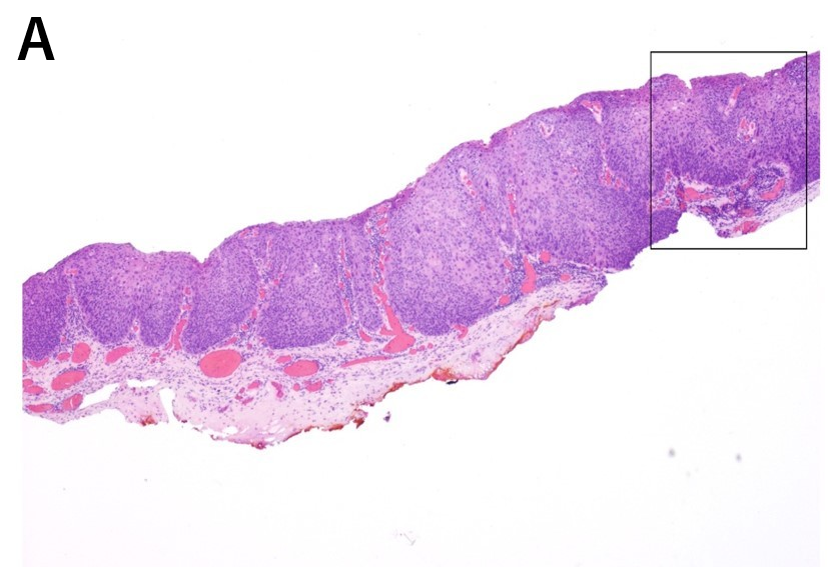
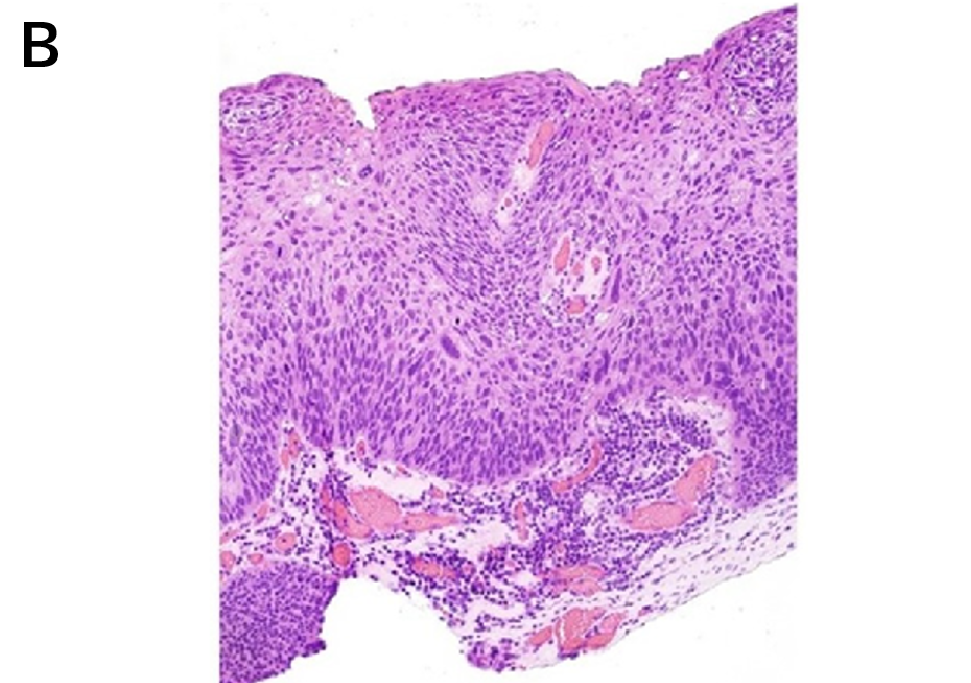
H&E view of the specimen (magnification 4x, A and 10x, B), obtained by an excisional biopsy, in term of subligamental cordectomy, by transoral CO2 laser microsurgery. The pathologic diagnosis is a well-moderate differentiated invasive squamous cell carcinoma; the depth of infiltration is 0.22 mm and all margins are clear of neoplasia. No risk factors, as perineural invasion or lymphovascular invasion, are observed.
The final pathological staging is confirmed to be a glottic SCC pT1a R0.
- Content Type