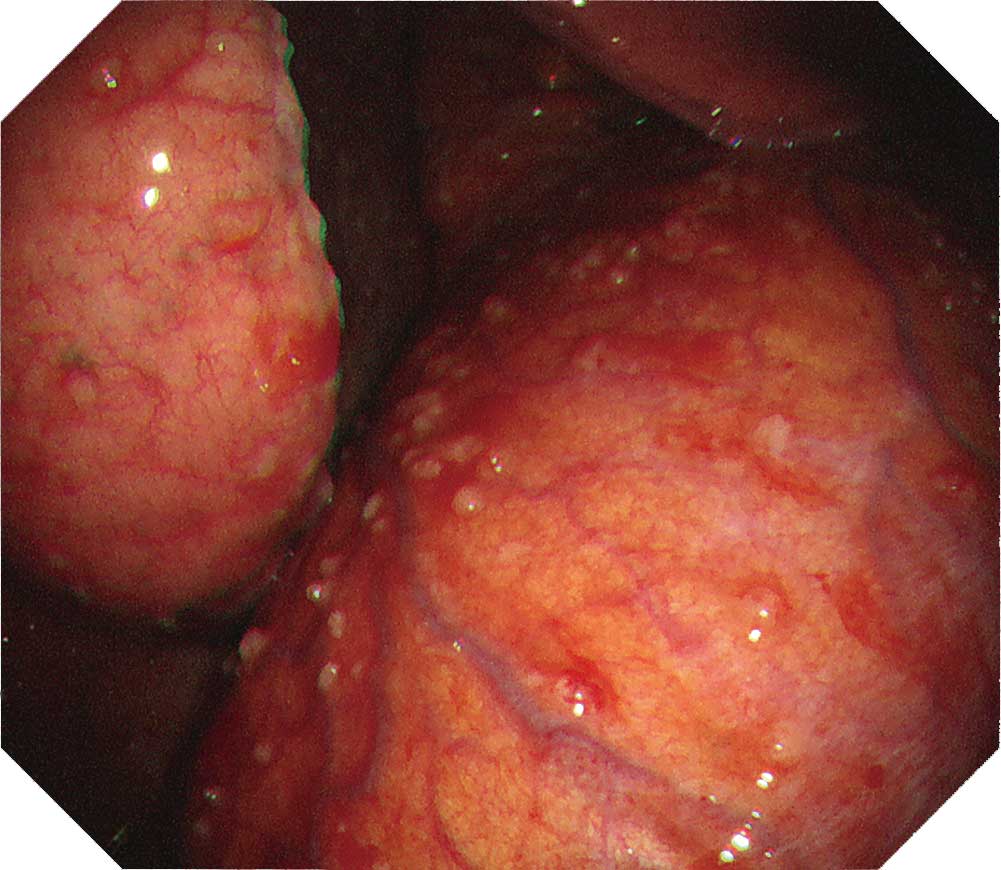
Carcinomatous pleuritis
Satoru Ishii — National Center for Global Health and Medicine
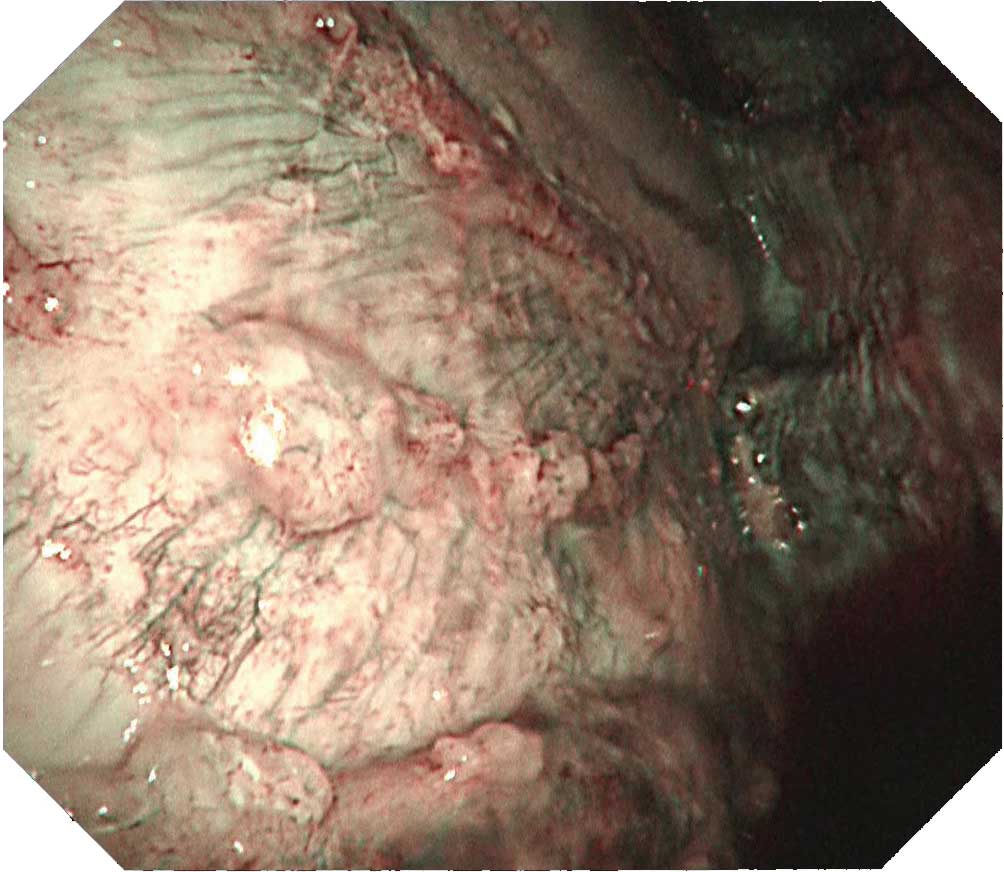
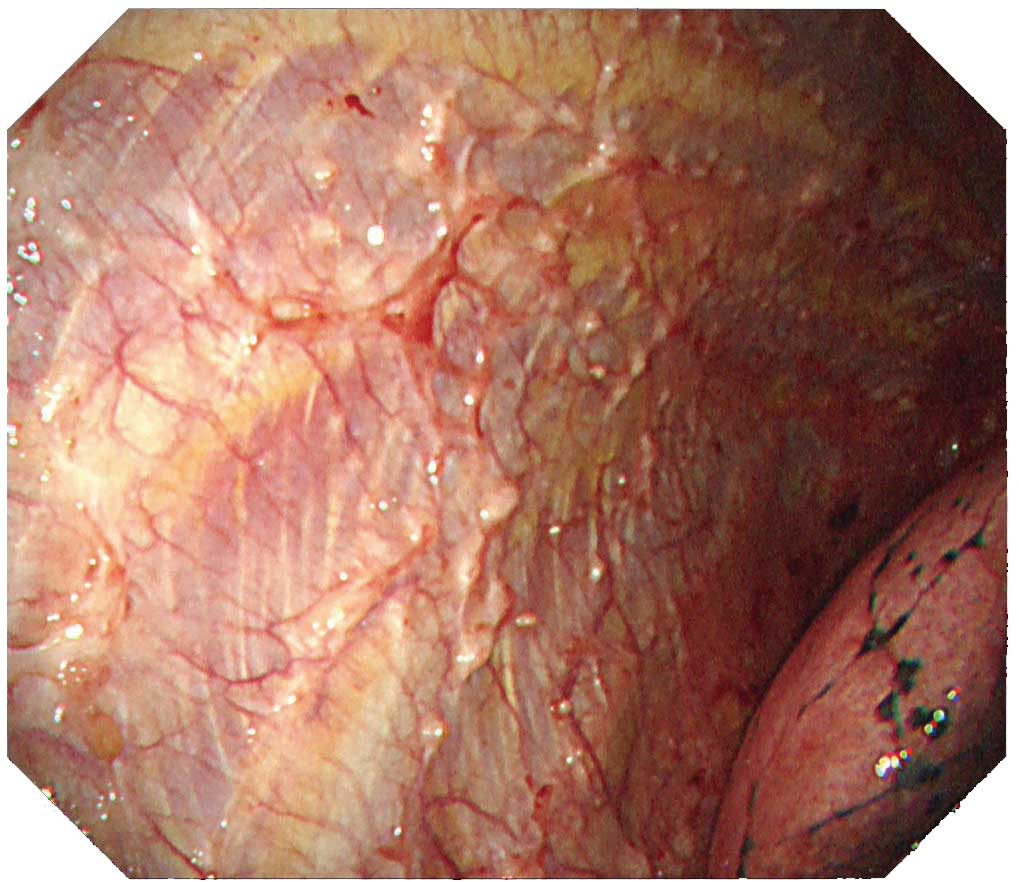
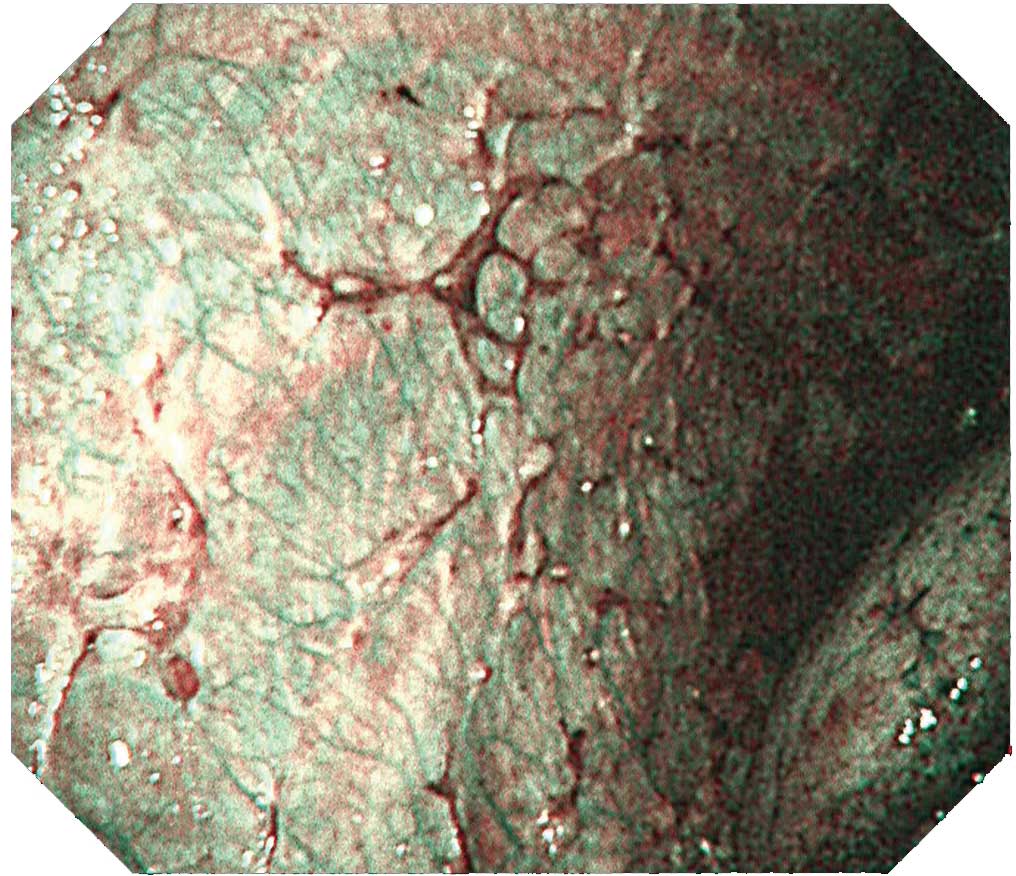
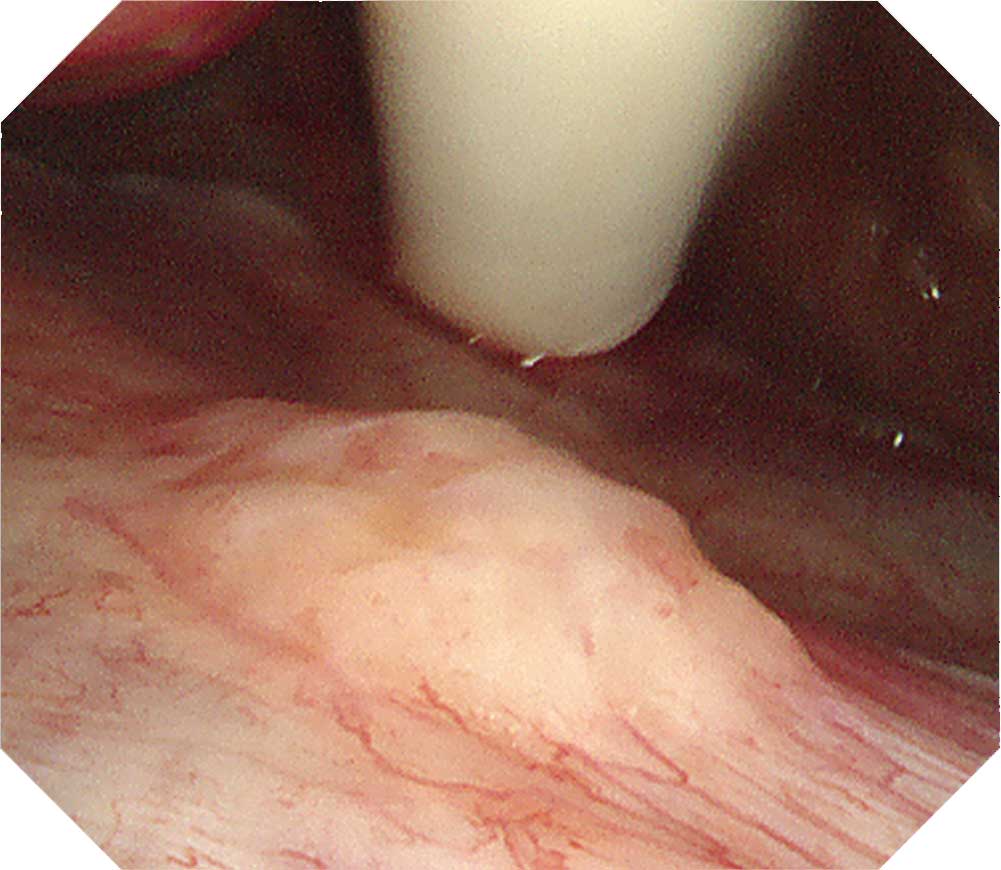
Case B-2 (NBI image)
The same site imaged with white light in B-1 is imaged with NBI. The irregular surface of the tumorous lesion now stands out clearly. Not only is the vascular distribution of the parietal pleura easy to visualize, the vascular distribution on the surface of the tumor can be clearly distinguished.Tip
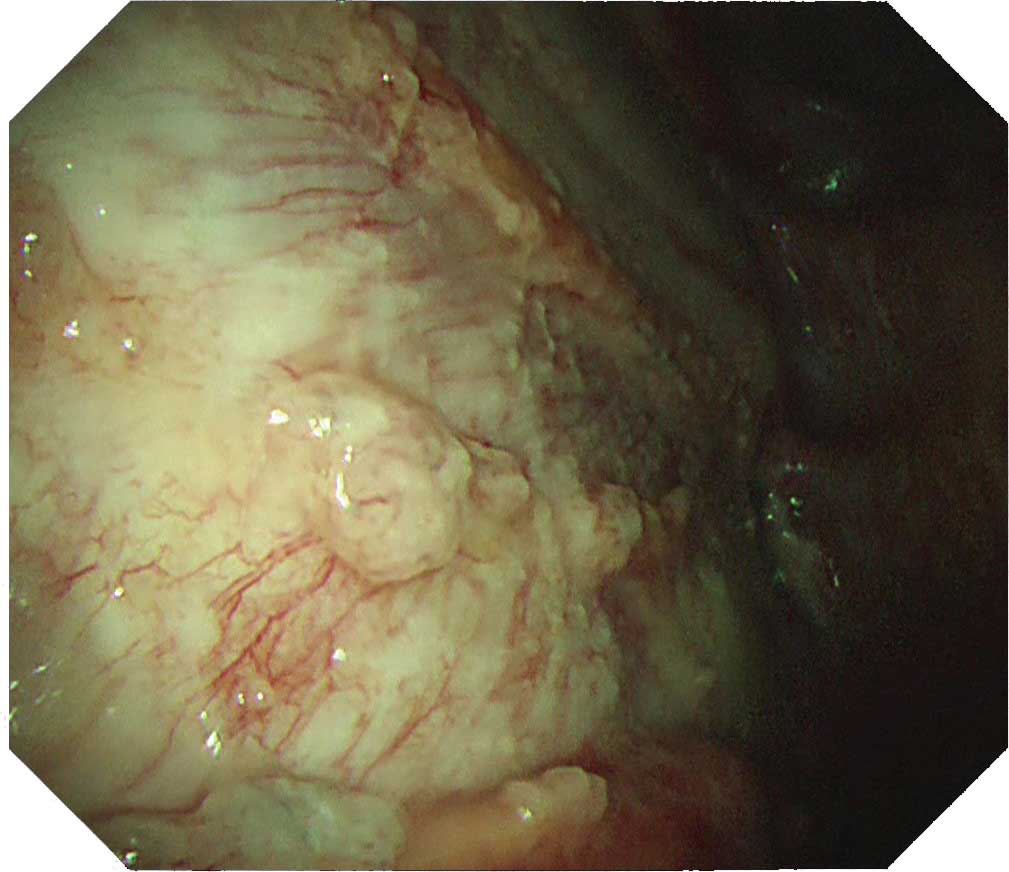
Carcinomatous pleuritis occurs in a diffuse form in many cases. But there are also localized cases. So care is required when observing it. The LTF-H290 features an expanded bending angle of 180° in its distal flexible section, which makes it possible to observe the vicinity right below the entry port. Even when the scope tip is angulated at 180°, biopsy forceps can be inserted through the channel and biopsy can be performed. After observing throughout the thoracic cavity, decide from which region a sufficient amount of tissue can be safely obtained.
Protruded lesions are often recognized in carcinomatous pleuritis Although there are many tumorous lesions, sometimes granular and small nodular lesions are also seen. NBI can clarify the irregular surface of the tumorous site and the edges of the site. When using NBI, check the vascular distribution on the parietal pleura, as well as whether large vessels are scattered inside the tumor.
Tuberculous pleuritis
Takayuki Kaburagi — Ibaraki Prefectural Central Hospital and Cancer Center
Tip
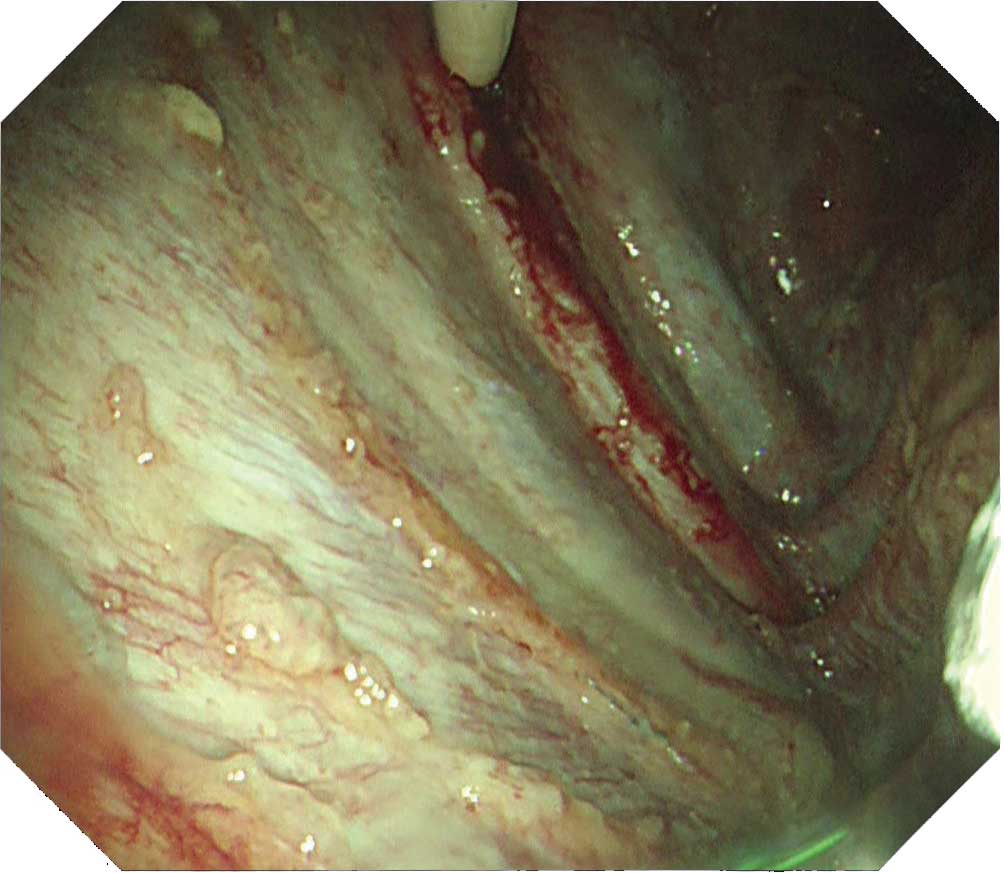
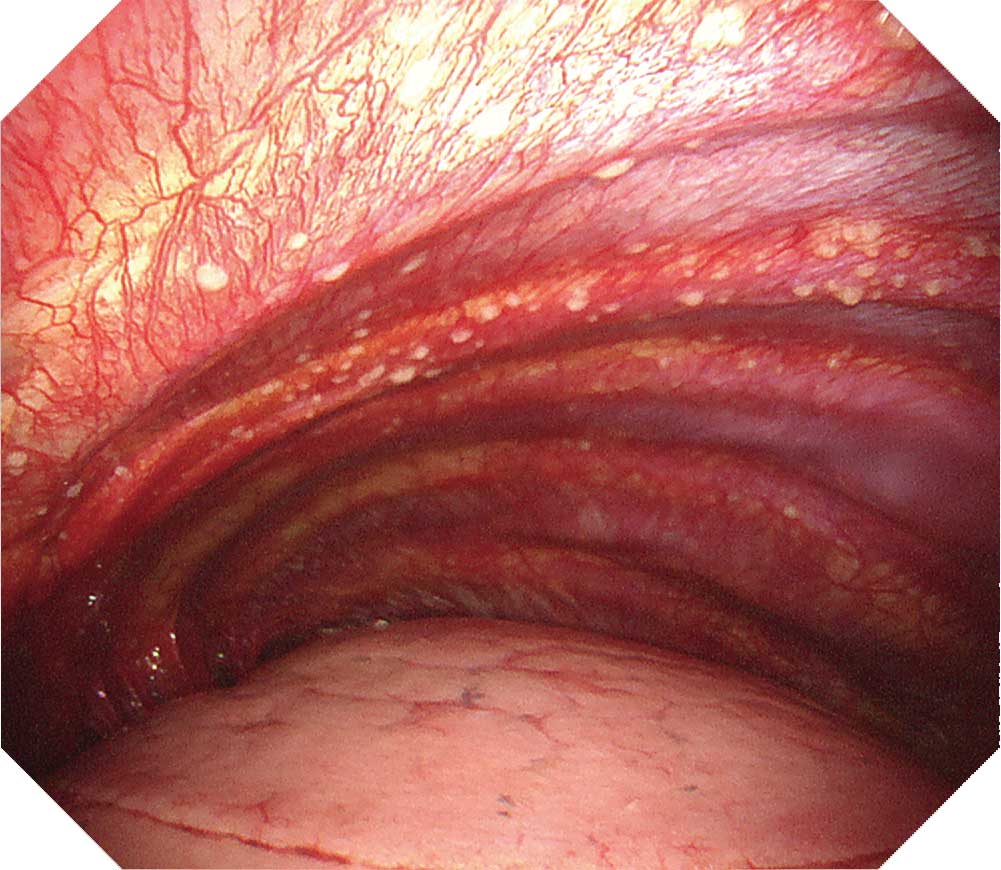
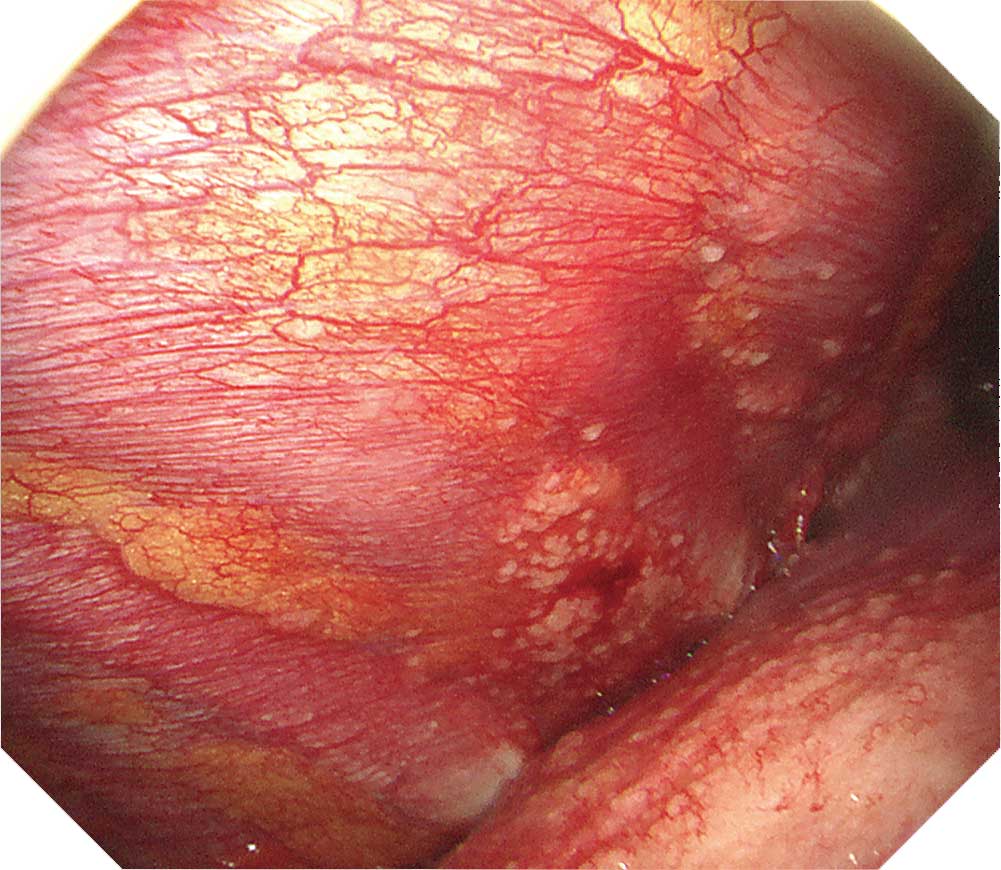
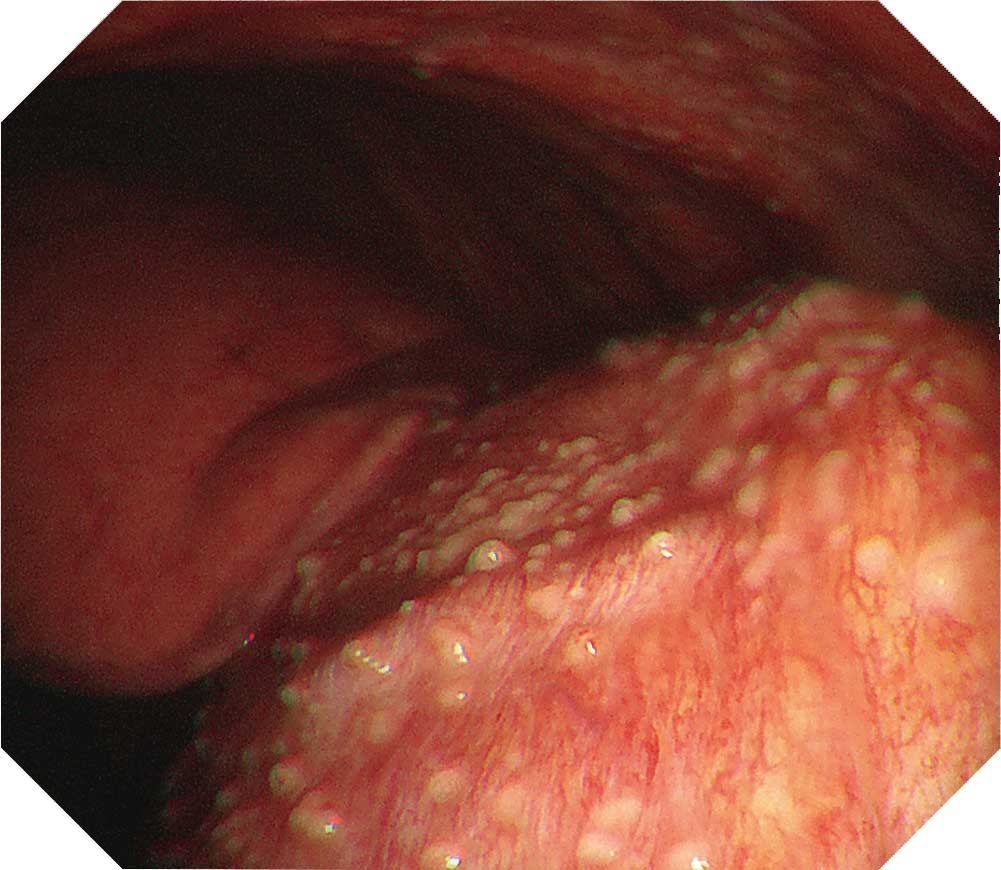
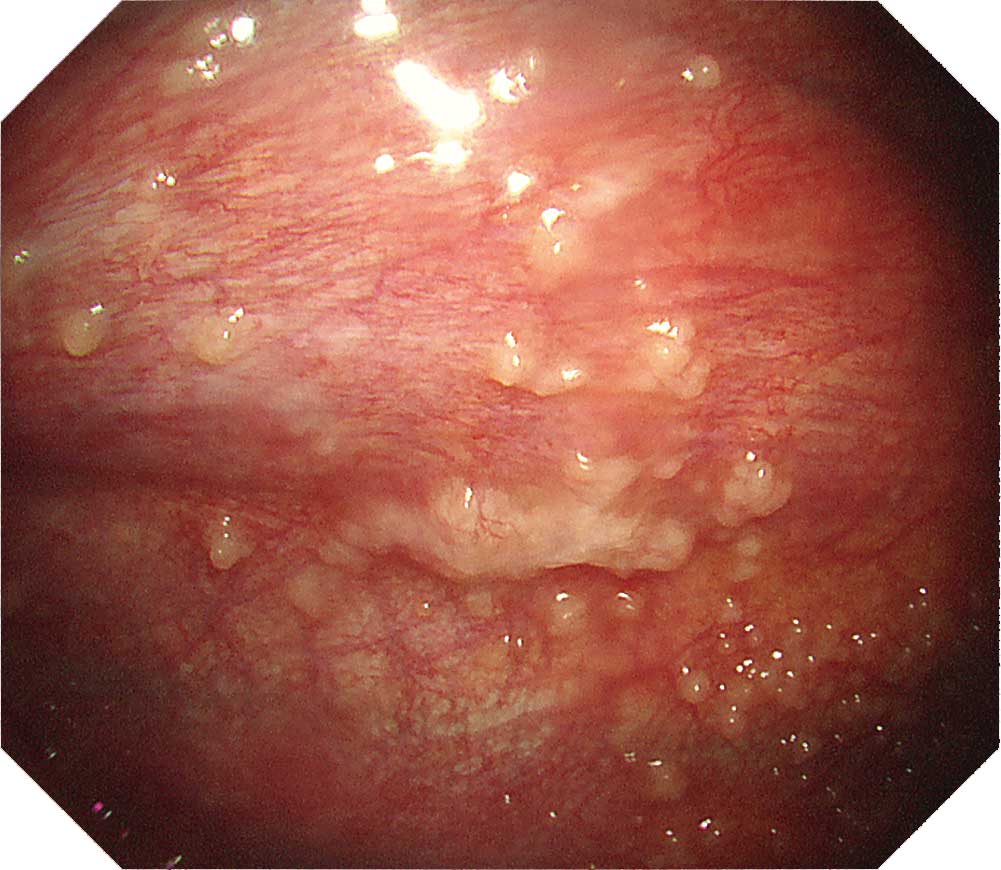
When observing the thoracic cavity in thoracoscopy under local anesthesia, you will often see a diffuse distribution of small whitish nodules slightly tinted with yellowish and pinkish colors ranging in size from 1–5 mm on the parietal pleura. Pleura at an early stage from onset appears red and slightly thickened. Congested dilated vessels can also be seen in the pleura. As time elapses, the nodules on the pleura exhibit confluent tendencies. Over a longer period of time the characteristic nodules will be buried in the thickening pleura.
When a nodular lesion is biopsied endoscopically, epithelioid granuloma is detected in most cases. If inflammation inside the thoracic cavity increases, it will become difficult to biopsy the parietal pleura, making an aggressive approach desirable at an early stage using thoracoscopy under local anesthesia.
- Content Type